To achieve and maintain a market leading position, organisations rely on the effective deployment of technology. But with an ever changing technological landscape it is only those organisations who embrace and adopt new and emergent technologies who will succeed in the long term.
We can consider a business as a living being, interacting constantly with external factors in the global environment in which it operates. The beating heart of any organisation can be compared to its data, and more specifically its database. So what tools play a role in keeping performance high, and ensuring the agility of the organisation as it responds to these external factors?
A poor database infrastructure will have a direct impact on the health of the company, how it performs and how it responds in the context of global events, market changes and competition.
One of the most robust and intelligent enterprise grade relational database management systems is SAP HANA. In this article we’ll look at some of its capabilities, and how they can be harnessed to deliver a competitive advantage to organisations where it is implemented effectively.
SAP HANA is well known for being an in-memory RDBMS that combines online analytical processing (OLAP) and online transactional processing (OLTP).
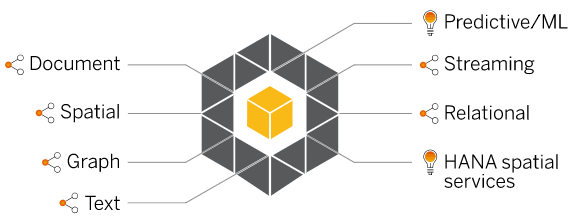
In addition, SAP HANA acts as a powerful data platform for the modern Intelligent Enterprise via:
Image 1
For the purposes of this article we’ll look specifically at a subset of SAP HANA’s capabilities, namely Spatial Data Processing, Machine Learning, and Predictive Analytics.
Spatial Data Processing (Cloud)
SAP HANA Spatial services provide a set of services such as Earth Observation Analysis; Spatial Data Management; Mapping API; Object Detection; Weather API and many others, all of which run on the SAP Cloud Platform.
These services focus on the collection, the storage, the processing and consumption of geo-reference data from public sources such as the European Space Agency or the German Weather Agency as well from private sources like customer images and business data.
They can readily be implemented in Intelligent Farming & Smart Harvesting by uploading drone images of the plantation fields and returning the locations of the products ready to harvest.
Image 2
The image above is an example of a palm tree detector based on drone images uploaded to the Object Detection API.
Machine Learning and Predictive Analytics
Nowadays, the ability to extract insights from large scale datasets is one of the most competitive assets available to companies.
The in-database Machine Learning capabilities in SAP HANA enable Machine Learning and Predictive Analytics to be integrated into business processes, operating with minimal execution latency and in real time, regardless of the size of the database or the complexity of the predictive model.
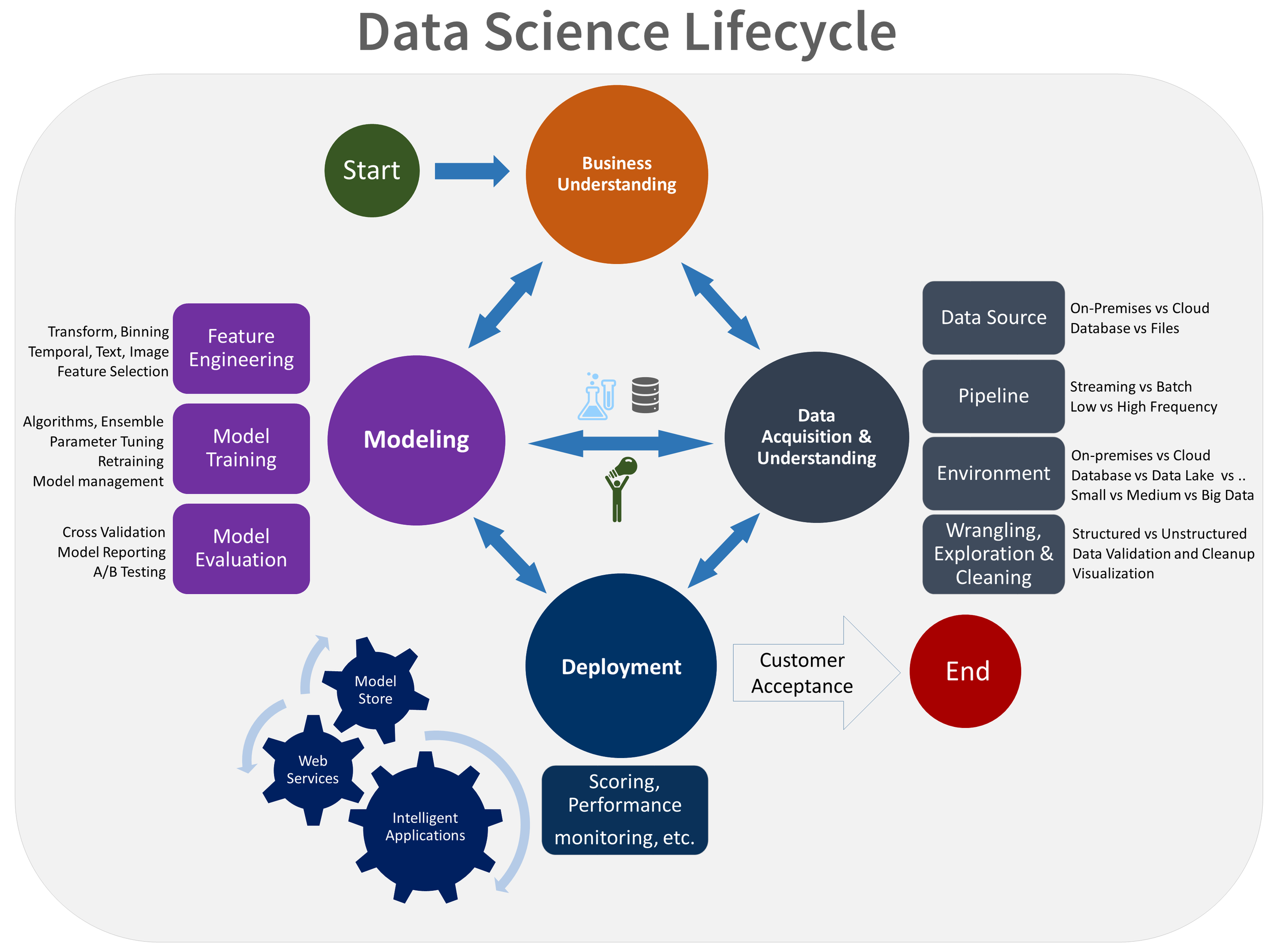
The SAP HANA architecture also facilitates the Data Science model building lifecycle, enabling high-performance access to, and manipulation of, all enterprise data.
Image 3
These tools take advantage of in-memory processing to run statistical and machine-learning algorithms which are able to rapidly generate and evaluate models.
The Predictive Analysis Library (PAL) delivered via SAP HANA defines functions that can be called from within SQLScript procedures to perform analytic algorithms. The latest version of SAP HANA has nine data-mining categories:
Clustering (K-Means | K-Medians | SOM | …)
Classification (AUC | KNN | Naïve Bayes | …)
Regression (Polynomial Regression | Exponential Regression | …)
Association (Apriori | FP-Growth | KORD)
Time Series (ARIMA | Trend Test | Forecast Smoothing | …)
Pre-processing (Binning | Partition | Posterior Scaling | …)
Statistics (Grubb’s Test | Quantile Function | Distribution Fitting | …)
Social Network Analysis (Link Prediction)
Miscellaneous (ABC Analysis | Weight Score Table)
PAL also provides machine learning algorithms that learn and update models on the fly, so that predictions are based on a dynamic model.
Applying machine learning algorithms to live stream data can be a major contribution in an Industry 4.0 environment where data from machinery can be obtained through IoT devices and predictions about failures can be updated in real time allowing proactive instead of reactive responses, and therefore enabling significant cost savings.
With the considerable speed of change associated with these technologies, due mostly to the open-source effect, companies need to be able to adopt and implement them quickly and effectively if they want to survive in today’s ultra competitive environment.
SAP HANA enables that, and furthermore provides a platform that can be used not only by Data Scientists but also by Business Analysts.
By abstracting the technology in such a way that users don't need to have subject specific knowledge in data science, users with a good understanding of their data are able to utilise the predefined models available in SAP HANA or to access the models deployed by in-house Data Scientists.