Learn how SAP Data Warehouse Cloud uses SPACES to allow you to streamline data governance and share data and analytical models across distributed teams without delay.
Businesses today face difficulties when it comes to implementing a data warehousing solution. The enterprise needs to ensure data quality, data governance, and security of data. But smaller sections within the organization such as departments, working teams, and others need maximum agility.
These smaller groups have their own datasets, which may partially overlap with the organization’s central repository. This often includes their marketing data, social media data, and other sources of data that require their own analytical approach, specific reports, and data models.
A large organization will typically have a traditional enterprise data warehouse, which will provide services such as data model consolidation, data governance, and lifecycle management. In this kind of environment, the IT department cannot give access to the central repository for other smaller groups in the organization.
This often results in a situation where those groups start building their own data models. Consequently, the IT department has limited access to their own data repositories - leading to a big question mark over data governance. If the IT department isn’t fully able to assure data quality, integrity, security, and so forth, then in effect this leads to the absence of a centrally governed data model.
To mitigate and overcome this type of scenario, SAP has developed a new concept called SPACES in the SAP Data Warehouse Cloud (DWC).
SPACES – DATA GOVERNANCE
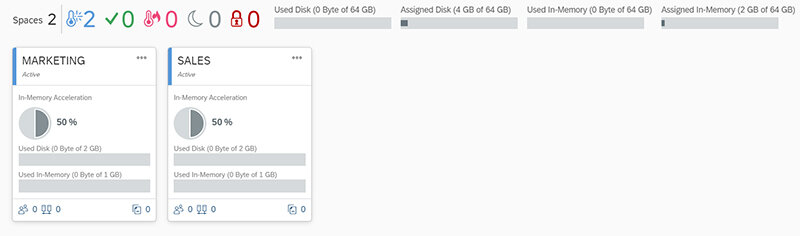
In SAP Data Warehouse Cloud Spaces allow you to create an environment to manage resources and customize the user experience in a way that meets your individual business requirements. Spaces are isolated and can be assigned quotas for available disk space, CPU usage, and memory usage. You can assign users and connections to a specific space and adjust the storage capacity. In addition, Spaces can help you to perform activities such as data modelling, data integration and story building.
In Spaces, data governance plays a major role - but before getting into the details of data governance let’s look at how to create the Spaces on our DWC tenant using the following SAP reference link.
https://saphanajourney.com/data-warehouse-cloud/resources/create-spaces/
Each Space is isolated but still connected to the central repository, central models, security, etc. In this way, the Spaces concept overcomes the absence of a centrally governed model. Each individual group in the organization can create their own Space, connected to their own data sources and allowing them to build analytical models and generate specific reports.
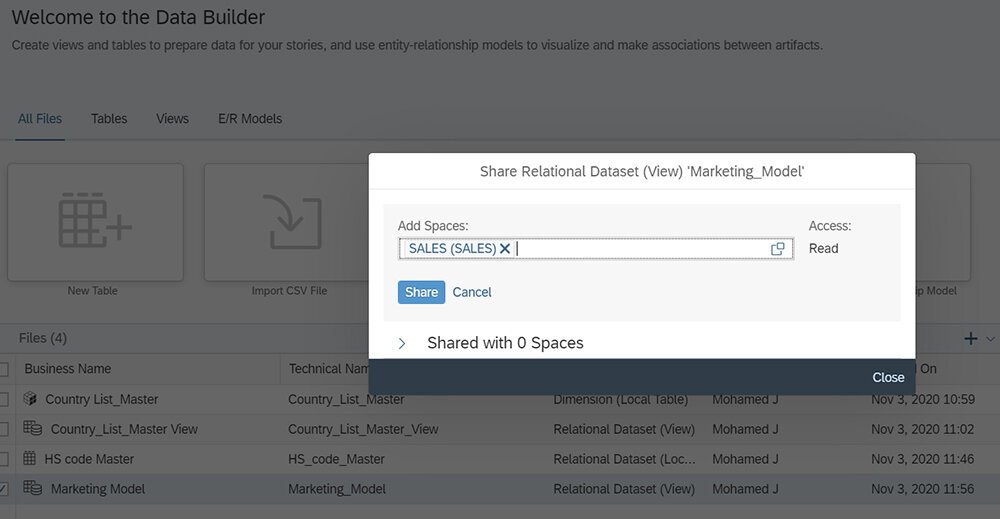
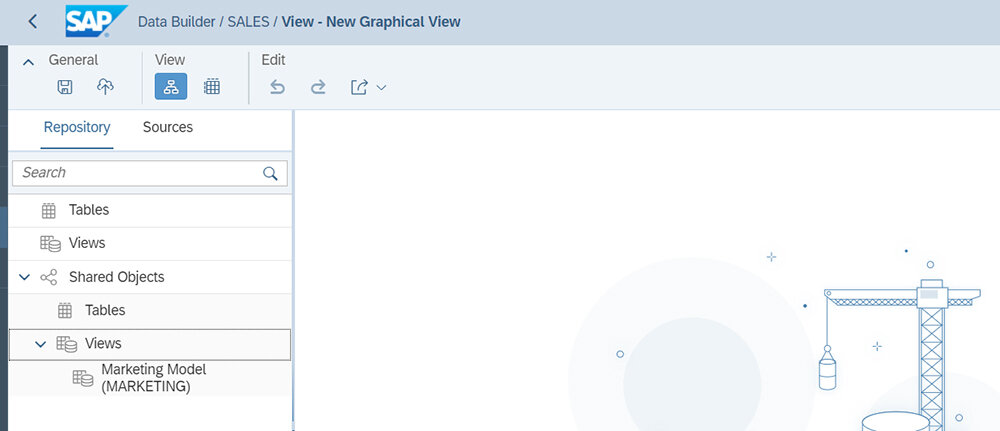
IT can expose any model from one Space to another using read access so that a user from another Space can access the shared model without modifying it. As an example, a marketing model created under the Marketing Space can be shared with the Sales Space - with the sales team automatically being granted read access.
A user from the Sales Space can then start building their own model, based on the model provided by the IT team from the Marketing Space. This results in a new joined model. Now we have a data map between the centrally governed model and a separate departmental mode running its own data warehouse which is a perfect example for maintaining central data governance within the DWC.
To look at another example - suppose the organization has an on-premises SAP HANA-based large data warehouse with excellent data along with the data model. They have made a continuous investment in generating cleansed consolidated data which is kept continually up to date.
Within this organization, there might be many business units or small functional groups who wish to access that data. But the central resources are limited, and it’s not feasible to provide access to all of the functional groups or business units who might request it.
So as we’ve discussed above, these small groups end up creating and managing their own data warehouse which cannot be centrally governed by the IT team - an unwanted scenario.
In this case, SAP DWC is the perfect solution. It allows you to create a connection with the organizational central data repository to get the specific amount of data which the business unit or functional group needs, and then publish the model to their individual Space in the SAP Data Warehouse Cloud. The replication of data is quick and efficient, meaning that with very little delay the small business unit can build whatever analytics model or reports they need, within the Data Warehouse cloud and without modifying any data on the on-premise Datawarehouse.
Now the power of Spaces in ensuring effective data governance becomes clear. Users in various groups are getting all the flexibility they need, but the integrity of the central repository and model is still preserved.
With the Spaces concept, we can allow each business unit or functional group within the organization full access to a centrally governed data warehouse, which is normally not an option. So, the group has full ownership, but the organisation, and central IT team, maintains central governance, data quality and security. The age-old difficulty between agile and centrally governed data is solved at last.
Feel free to contact us if you would know more about data governance on Spaces in DWC or to implement the SAP Data Warehouse cloud as your enterprise data warehouse.
Our next article will focus on how easily you can connect and integrate the SAP Data Warehouse Cloud with your on-premise systems - watch this space!